How much does it cost to build an energy efficient home
There’s a lot to think about when building an energy efficient home. It can be hard to keep track of all the different things that have an impact on your energy bill and don’t get taken into consideration when building a new home. From choosing the right insulation system to finding smart ways to use electricity, there’s a lot of information to know in order to design a home that is going to use as little energy as possible. You’ll want to make sure you’re considering everything, so I’ve put together an article with some of the most common tips I’ve seen people use.
Are you currently in the process of thinking about designing an energy efficient house, how energy efficient is my home, how much energy does a home need? If you are then don’t forget to check out the information below! When it comes to designing an energy-efficient home, there are quite a few important things that you’re going to need to think about.

How much does it cost to build an energy efficient home
The costs of building an energy efficient home vary greatly depending on the size and type of your home. It’s important to understand that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to building an efficient home. The cost of building an energy efficient home depends on many factors, including the location of your home, the size of your lot and the design of your house or apartment.
How much does it cost to build a new house?
The average cost of building a new house in 2016 was $319,100, according to U.S. Census Bureau estimates. This number includes all types of homes built across America in 2016: single-family detached homes, multi-family units and condominiums. The median price for all three types was $315,800.
What is included in home energy costs?
The cost to build an energy efficient home can include everything from choosing the right windows and insulation to adding solar panels on your roof. But what exactly are these things going to cost you? What are some other hidden costs that might come up during construction?
How energy efficient is my home?
The cost to build an energy efficient home can vary depending on the size and location of your property, the number of rooms you want to include in the design and your budget. The average home in the U.S. uses approximately 1,500 kilowatt hours per month or 10,000 kilowatt hours per year. The cost to build an energy efficient home can range from $1,200 to $20,000 for a 2,000 square foot home with a three bedroom and two bath plan.
What is included in home energy costs
The cost to build an energy efficient home includes:
– Foundation: This is the base of your house that supports its weight and stability. Foundations are usually poured concrete or poured concrete block with rebar reinforcement wire inside it. They come in many different shapes (flat slab) and sizes (rectangular). The foundation price varies depending on its size and complexity. The cost for a slab on grade foundation starts at about $6 per square foot for a basic flat slab up to $15 per square foot for a complex foundation system such as crawl space or basements that require excavation work before pouring concrete
The amount of money you’ll spend to build an energy efficient home depends on many factors. The size and style of the home, the local climate and the materials used to build it all come into play.
The average cost of building a new home in the U.S. is $250 per square foot, according to data from the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB). That’s based on homes that are 2,100 square feet with three bedrooms and two bathrooms — not including land costs or labor costs for things like landscaping and flooring.
Home energy costs can vary widely depending on where you live, but we can give you some general estimates based on geographic location. According to Energy Saver, an Energy Star program run by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), heating accounts for about half of a household’s total energy use each year, so it’s important to consider how much heating will cost when building an energy efficient home.
Home energy costs are a significant portion of monthly expenses for most homeowners. That’s why it makes sense to make your home as energy-efficient as possible.

Energy efficiency is one of the most important things you can do to reduce your energy bills and improve the comfort and safety of your home. There are many ways to save energy, but the easiest way is by choosing an ENERGY STAR certified home when you build or buy your next home.
You can calculate how much money you will save on utility bills with our Home Energy Saver tool. The results will vary depending on local utility rates, building size and configuration, climate zone, weather conditions and other factors.
How much does it cost to build an energy efficient home?
The cost of an energy-efficient home is a complicated question. In general, the more energy-efficient your home, the greater its resale value. However, as with any major construction project, there are many variables that can significantly affect the overall cost of building an energy-efficient home. The type of materials used, the size and layout of your house and even where you live can all impact how much it will cost to build an energy-efficient home.
But what if you want to know how much money you’ll save on utility bills over the life of your new home? That’s a different question altogether — and one that is much easier to answer. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that homeowners who invest in high-efficiency windows, doors and insulation save about $100 per month on their utility bill after installation compared with similar homes built before 2000 that don’t have these features.

How energy efficient is my home
The average U.S. home uses about 91,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year, which is equal to about 11,000 pounds of coal or 2.6 million cubic feet of natural gas. This amount is enough energy to power all the lights in a typical American home for more than 2 months.
Energy efficiency is one of the most cost-effective ways to save money on utility bills and reduce dependence on foreign oil. It also helps protect our environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to global warming. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that if every American home were as energy efficient as today’s average new home, we could prevent 1.2 billion tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year — equivalent to taking 159 million cars off the road!
If you’re considering making improvements to your home’s energy efficiency, take a look at these questions:
What is included in home energy costs?
How much energy does a home need?
House energy costs are made up of a variety of factors. The most obvious is the price of electricity and natural gas. But there are other costs that you may not be aware of:
Energy Star appliances, windows, and HVAC equipment can save you money on your electric bill by using less energy to do the same job as older models. And if you use renewable energy sources like solar or wind, you’ll also reduce your carbon footprint and make an impact on climate change.
How much energy does my home need?
The amount of energy a home needs depends on its size and the number of people who live in it. A smaller house will require less energy than a larger one, even if both are occupied by the same number of people. If a house has poor insulation and inefficient heating or cooling systems, it will require more energy than one with better insulation and efficient HVAC equipment.
What’s included in home energy costs?
Homeowners pay for two types of utilities: utilities used inside the home (electricity, water) and utilities used outside the home (natural gas). These utilities can include:
Home energy costs are broken into two major categories:
Energy consumption. This is how much energy your home uses to operate. It includes heat, cooling, water heating and lighting.
Energy efficiency. This is how well your home uses the energy you provide it with. It includes insulation, windows, doors and appliances.
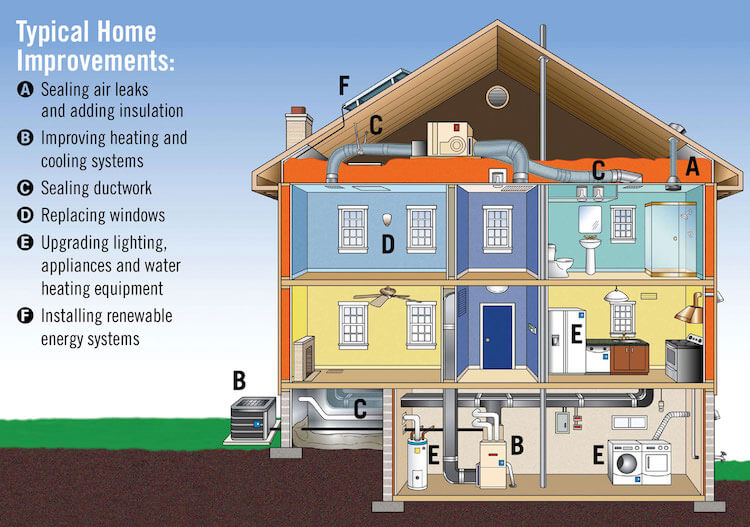
Energy consumption: How much does it cost?
The average American household spends about $2,200 per year on annual energy bills for heating, cooling and lighting their homes. That’s about 16% of the average household budget, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Keep in mind that this figure varies by region; some areas of the country have higher utility costs than others due to climate differences or other factors like population density or local infrastructure requirements (e.g., natural gas prices).
The average U.S. household spends about $2,200 on energy each year. This includes electricity, natural gas, heating oil and propane.
Energy efficiency is the most cost-effective way to reduce your energy costs. You can save money by making small changes in your home and turning off lights or appliances when you aren’t using them.
The amount of energy needed for a home depends on its size, age and location. You can estimate how much energy your home uses by comparing it to similar homes in the same neighborhood or city.
The average new home uses about 15 percent less energy than an existing home built before 1980. The Energy Star program provides ratings for new homes based on their energy performance in comparison to national averages for comparable homes built before 1990
The Energy Star program also provides ratings for existing homes based on their energy performance in comparison to national averages for similar older homes
The cost of energy is a major consideration for both homeowners and renters alike. The cost of energy varies depending on where you live, how much energy you use, and the type of fuel or electricity used. Homeowners can reduce their monthly utility bills by making changes to their homes and their lifestyles.
Energy-efficient homes use less energy than other homes, so they cost less to heat and cool. They also can save money by reducing the need for expensive repairs due to poor insulation or leaking windows and doors.
In addition to saving money on your energy bills, there are other benefits to having an energy-efficient home:
Lower utility bills — A well-insulated home that uses natural lighting will use less electricity or natural gas than an older home with leaky windows, drafty doors and poorly insulated walls. Energy efficiency upgrades such as replacing windows with ones that have low U-factors (the rate at which heat escapes through glass) will also help lower your utility bills.
Lower risk of fire — The risk of fire increases when heating systems fail in older homes that don’t have adequate ventilation. When installed correctly, modern furnaces will ventilate properly without posing a fire risk.